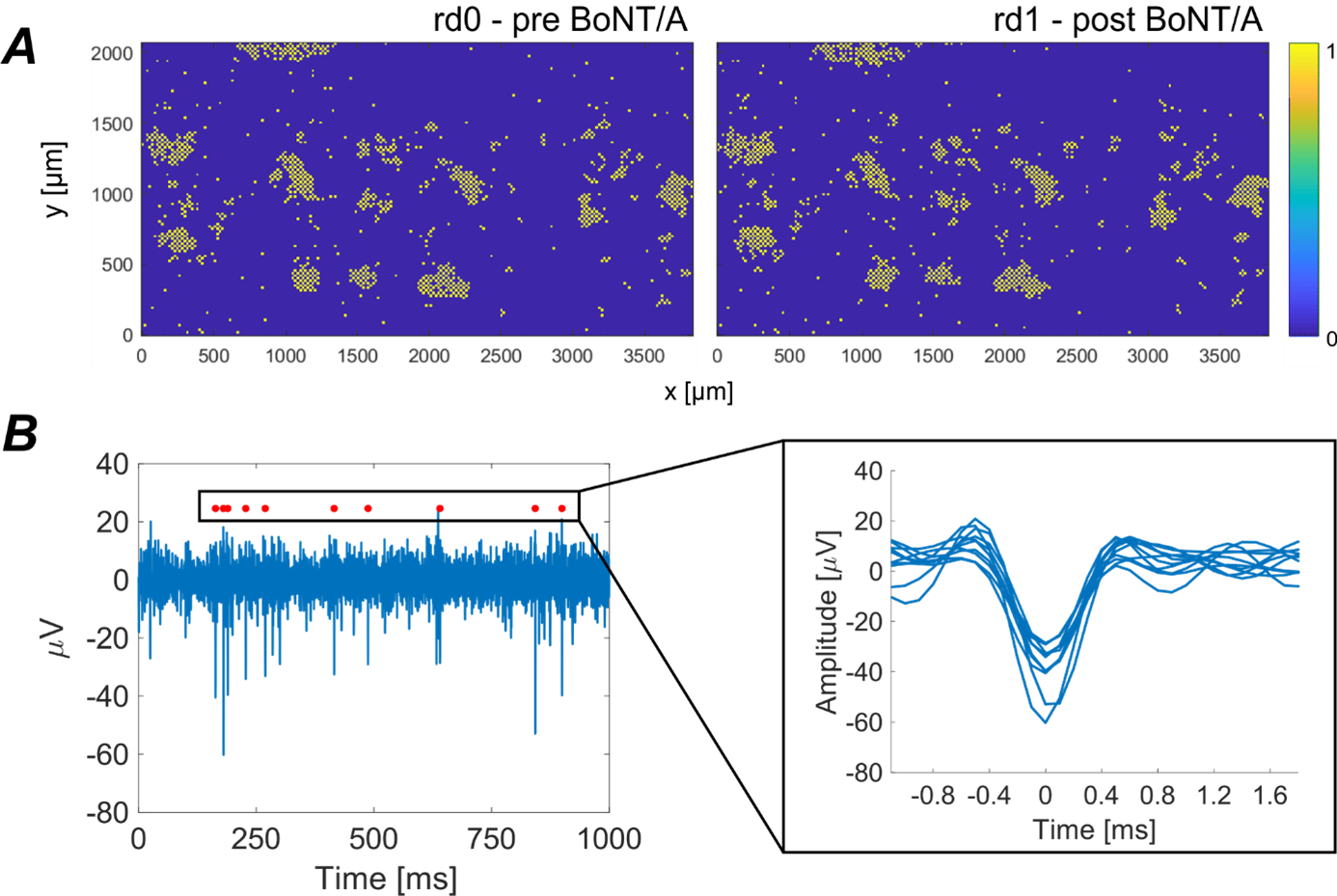
Botulinum toxin is not only a very dangerous neurotoxin, but also a frequently used drug in various medical fields. Apart from its muscle relaxant effect, the toxin has recently been used more and more in the treatment of pain, especially neuropathic pain. In order to investigate whether the voltage-dependent sodium channel, an important target in pain medicine, is also part of the pain-relieving effect of botulinum toxin, we conducted several studies.
We used various methods in the laboratory, different forms of application of the toxin and various cell types, including sensory neurons from stem cells. We can now say with relatively high certainty that the toxin does not influence, inhibit or interact with the sodium channel and therefore its use and its undisputed effect on neuropathic pain is independent of the sodium channel.
Analgesic effect of Botulinum toxin in neuropathic pain is sodium channel independent
Kesdoğan AB, Neureiter A, Gaebler AJ, Kalia AK, Körner J, Lampert A. Analgesic effect of Botulinum toxin in neuropathic pain is sodium channel independent. Neuropharmacology. 2024 Apr 23;253:109967. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.109967. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38657946.

![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/global/_processed_/a/e/csm_Homepage_Header_Mosaik_Digitale_Patientenakademie_a70850c5a6.jpg)
![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/klinik-neurochirurgie/_processed_/f/a/csm__DSC8610_810ca6c404.jpg)


![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/klinik-neurochirurgie/_processed_/c/6/csm__DSC6827_8235404da8.jpg)


![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/global/_processed_/6/9/csm_Homepage_Header_Zahnprofis_neu_11014e086b.jpg)



![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/global/_processed_/5/d/csm_Homepage_Header_Pflege-Podcast_Schichtwechsel_ohne_Schriftzug_unten_9cef107de3.jpg)
![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/klinik-gynaekologie-geburtshilfe/_processed_/b/f/csm_Header_DSC1044_2762f31c37.jpg)
![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/klinik-urologie/_processed_/d/1/csm__ME27551_9b86eb20f4.jpg)
![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/global/_processed_/7/4/csm_Homepage_Header_Podcasts_2023_668979f13b.jpg)