Forschungsprojekte
If you are interested in our research projects, feel free to contact the contact person or a member of our team.
Current Research Projects

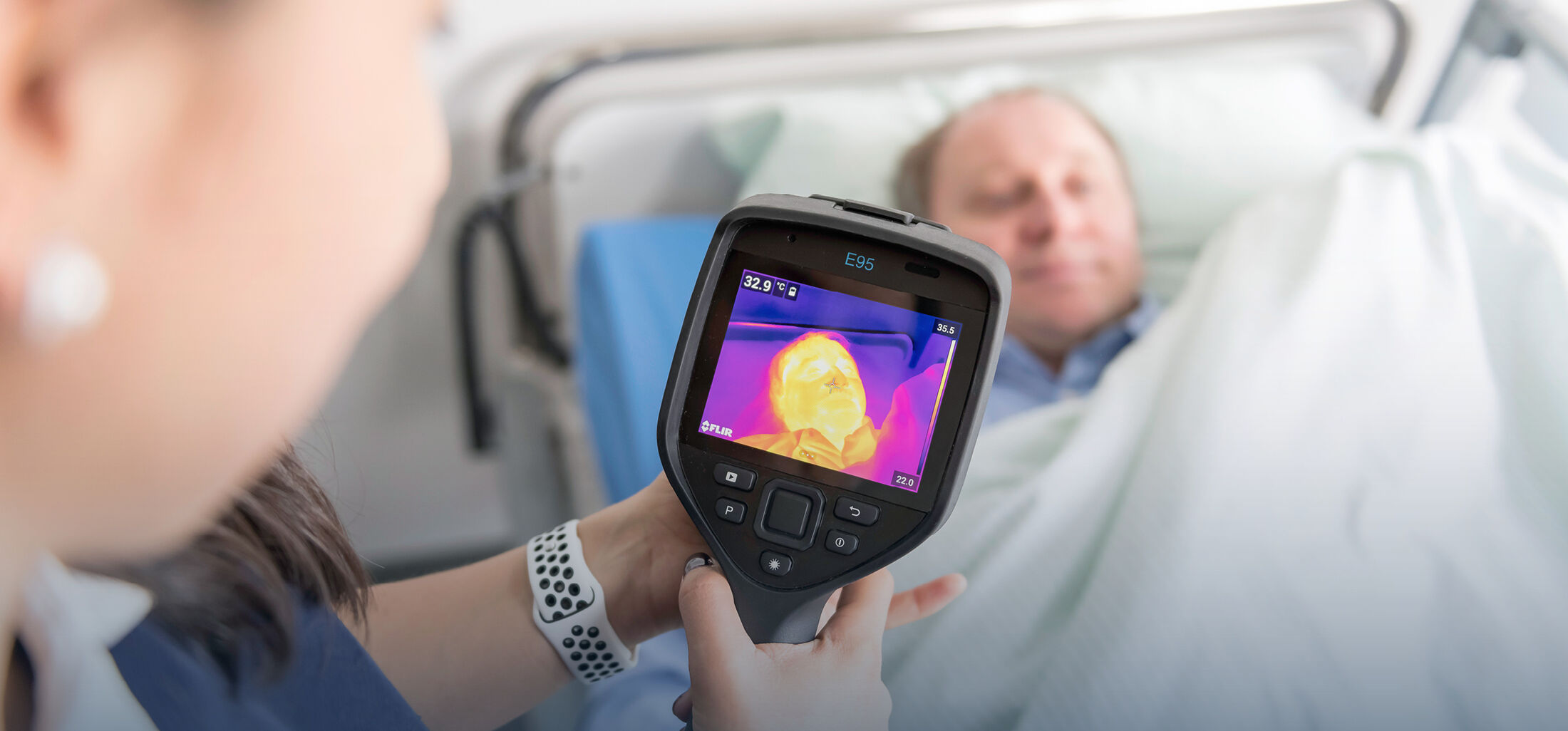
P04: Contactless monitoring of laboratory animals for the sake of home cage observation, refinement of anaesthesia and prediction of impending inflammation
The DFG research unit 2591 – a research consortium aims at defining a severity assessment framework for laboratory animals
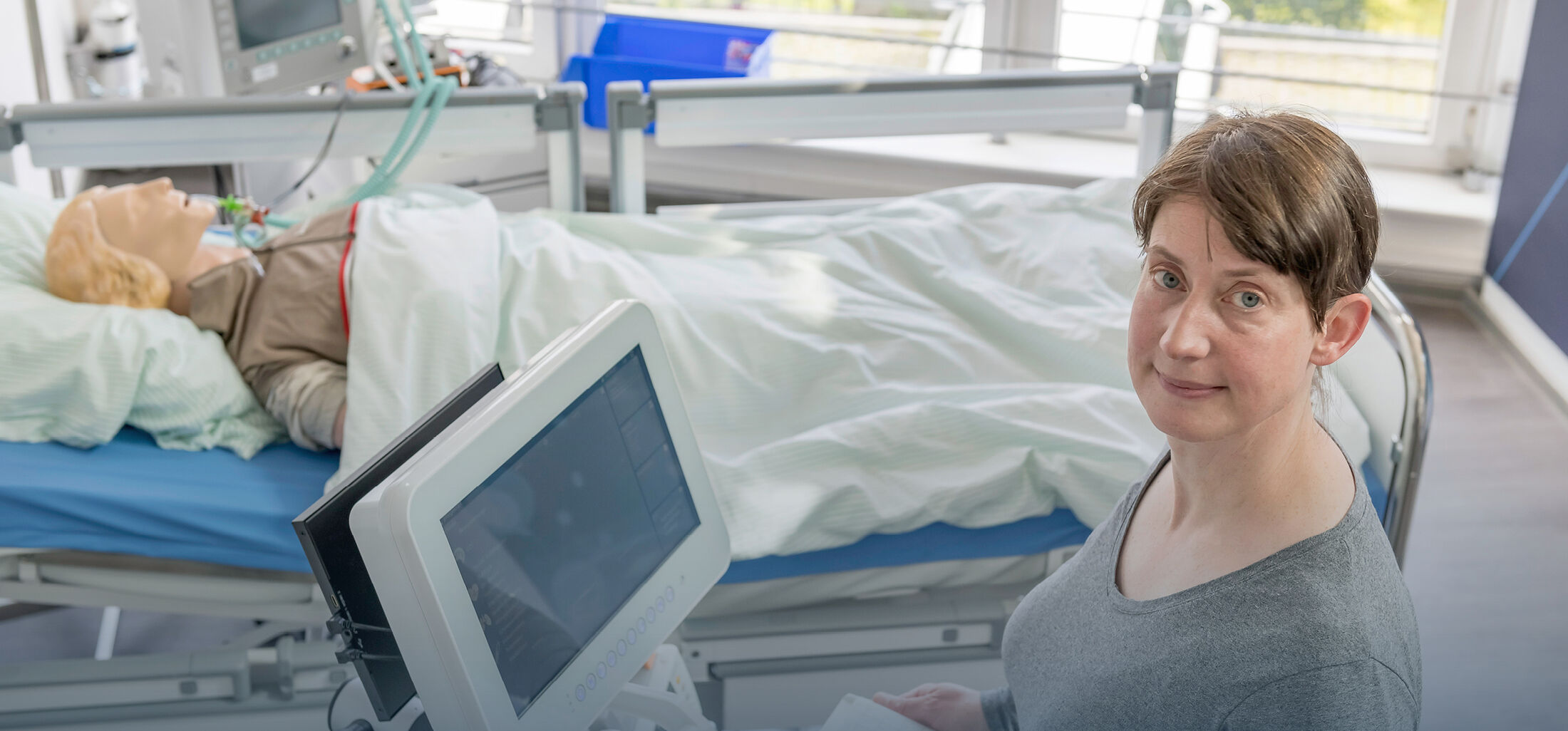
Patients of the intensive care unit must be constantly monitored regarding their circulatory system and health status. Therefore, they are connected to necessary measuring instruments with the use of electrodes and derivations which takes time and severely narrows the patient’s ability to move. Even patient transport is thereby made more difficult. Through the development of reliable, contactless measurement methods the patients’ ability to move can in this regard stay unrestricted and clinical procedures can be optimized.
This study targets a contactless assessment of the health status of experimental animals. Remotely, vital signs (respiratory rate, pulse, temperature) can be measured, signs of inflammation can be checked and perfusion imaging can be performed with the help of video sequences, radar as well as infrared- and colour cameras.
Further information can be found on: severity-assessment.de
Cooperation partners
The DFG project is part of a DFG research group with the common title: “Severity Assessment in Animal-based Research” (FOR2591)
- P01 Prof. André Bleich, Phd, DipECLAM (Hannover Medical School, Institute for Laboratory Animal Science and Central Animal Facility, Hannover) und Dr. Christine Häger (Hannover Medical School, Institute for Laboratory Animal Science and Central Animal Facility, Hannover)
- P02 Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. René H. Tolba, MD, PhD (Institute for Laboratory Animal Science and Central Animal Facility RWTH Aachen University, Medical Faculty)
- P05 Prof. Peter Gass, MD (Central Institute of Mental Health, Mannheim, Mannheim Faculty / University of Heidelberg, Mannheim/Heidelberg)
- P08 Prof. Dr. Fabian Kiessling, M.D. (Chair of Experimental Molecular Imaging, RWTH Aachen University, Medical Faculty, Aachen)
- P10 Prof. Ute Lindauer, Dr. med. vet. (Translational Neurosurgery and Neurobiology, Department of Neurosurgery, RWTH Aachen University, Medical Faculty, Aachen)
- P11 Prof. Dr. Heidrun Potschka, DVM (Institute of Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Pharmacy, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Munich)
- P12 Prof. Kerstin Schwabe, Phd (Laboratories for Experimental Neurosurgery, Hannover Medical School, Department of Neurosurgery, Hannover)
- P14 Prof. Dr. Stefan Treue (German Primate Center, Head of the Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory, Göttingen) und Prof. Dr. Alexander Gail (Sensorimotor Group, German Primate Center, Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, Göttingen)
- P15 Dietmar Zechner, PhD (Rostock University Medical Center, Institute for Experimental Surgery, Rostock University Medical Center, Rostock) und Prof. Dr. med. Brigitte Vollmar (Institute for Experimental Surgery, Rostock University Medical Center, Rostock)
- nP17 Dorit Merhof, Prof. Dr. Ing. (Institute of Imaging & Computer Vision, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen)
- nP18 Marion Bankstahl, Prof. Dr. (Institute for Laboratory Animal Science, Hannover Medical School, Hannover)
Contact
Dr.-Ing. Carina Barbosa Pereira (cbarbosapereukaachende)
Lucas Mösch, M.Sc. (lmoeschukaachende)
Lukas Breuer, M.Sc. (lubreuerukaachende)
Julianna Monissen (jmonissenukaachende)
Funding
Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Project duration: 10/2020 – 09 /2023
EULE - European UAV-assisted transport solutions for medical supplies
Medical goods, such as pharmaceuticals, blood and tissue samples, have to be transported between pharmaceutical dealers, hospitals and laboratories as quickly as possible. This represents a significant economic, logistical and ecological burden for our society.
The use of highly automated, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) and their extensive integration into medical operations can drastically increase transport efficiency, which offers enormous potential for improving medical care between cities and rural regions and promotes the digitalization-driven smart networking of medical logistics processes. In addition, roads can be relieved and pollutant emissions can be significantly reduced, since instead of cars or vans, purely electrically powered micro-aircraft optimized for the low payload can be used.
The main goal of this sub-project is to ensure the necessary integration into the processes of the participating medical "customers" (hospitals, laboratories, etc.). There is a risk that, in the case of complicated operation or handling, the effort will outweigh the benefits for the staff. This interface is intended to mediate between the customer's process system and the local platform of the UAS "MedPort". In addition to making it easier to use, role and data management is of great importance here, since the data is particularly worthy of protection due to its medical nature.
Cooperation partners
RWTH Aachen
FlyXdrive GmbH
Docs in Clouds TeleCare GmbH
City Aachen
Droniq GmbH
Aachen University of Applied Sciences
Vodafone
Contact
Sarah Veldemann, Ärztin (sveldemanukaachende)
Funding
Bundesministerium für Verkehr und digitale Infrastruktur
Project duration: 01/2022 – 12/2024
Website
RespCam.AI – Remote monitoring of breathing patterns and automatic classification using artificial intelligence for early detection of deteriorating health in patients
The respiratory rate (RR) is an important and at the same time sensitive indicator of the state of health. It is closely related to the acid-base balance and the oxygen consumption of the human body. However, various diseases and temporary conditions also influence the breathing pattern in different, sometimes very specific ways (frequency, rhythm, various time parameters such as inspiration-to-expiration ratio, curve shape of the volume and pressure curve, breathing depth or amplitude, etc.) . While these parameters can easily be measured via the ventilation tube in ventilated patients, the available measurement technology for spontaneously breathing patients is usually limited to monitoring the RR.
As part of this project, (1) thoracic excursions and air circulation are to be recorded using various camera systems (long-wave infrared and color cameras) as well as (2) analyzed and clinically evaluated using AI (neural networks and four expert systems) and (3) specific respiratory disorders will be diagnosed and possibly even predicted.
For this purpose, innovative algorithms for breathing curve extraction and breathing pattern classification are being researched. Therefore, a clinical study will be carried out in the recovery room of the clinic for anesthesiology, which will provide the data required for the development of the algorithms.
Cooperation partners
-
Contact
Dr. Ing. Carina Barbosa Pereira (cbarbosapereukaachende)
M.Sc. Lukas Ullmann (luullmannukaachende)
Funding
START – Forschungsförderung an der Medizinischen Fakultät der RWTH Aachen
Project duration: 09/2022 – 09/2024
VitalKITE - Vital Data Monitoring through an Innovative Camera-Based Technical Deployment Tool
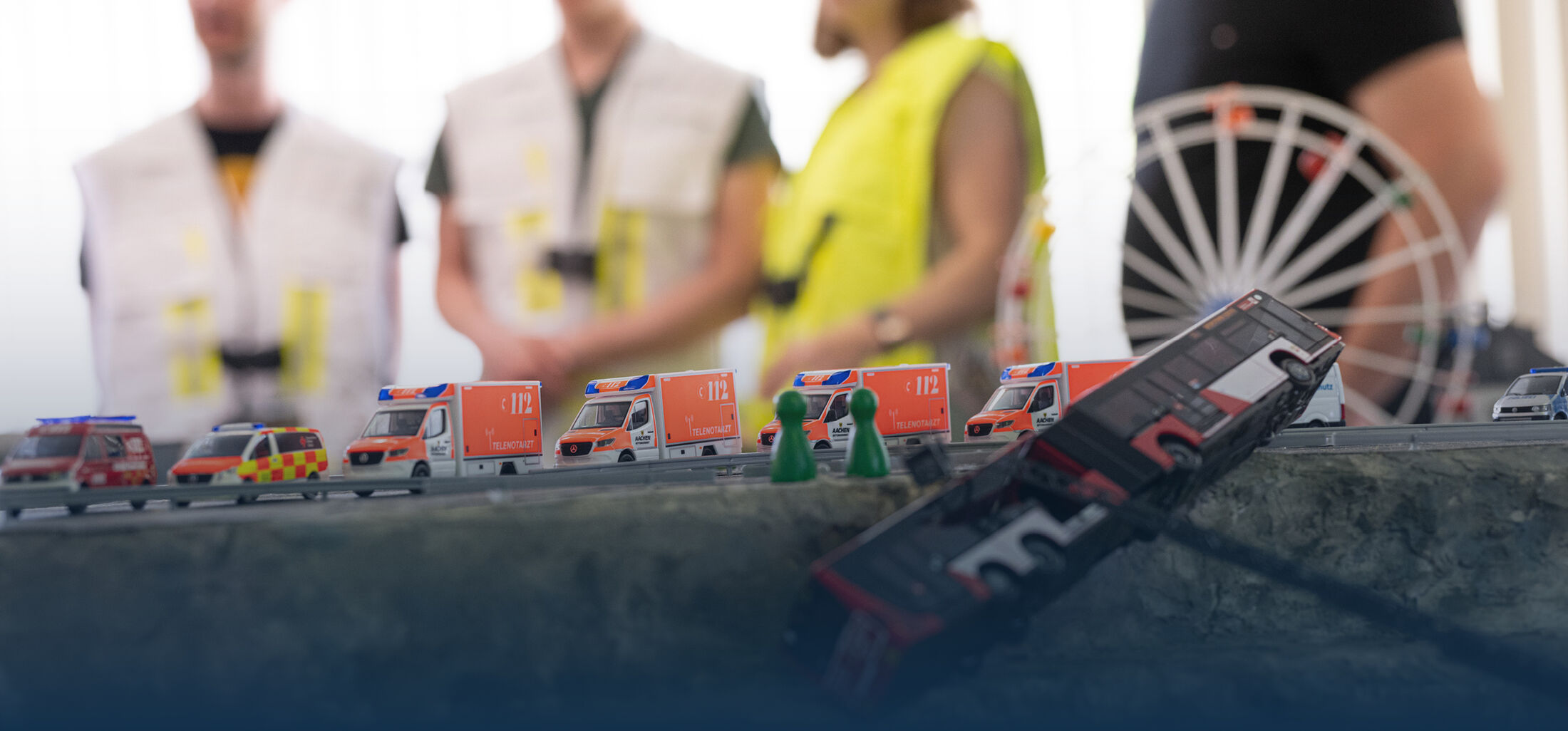
In large-scale disaster events in disaster and civil protection scenarios, the number of injured often exceeds the capacity of the emergency personnel. In such situations, medical care is ensured by setting up casualty collection points and patient holding areas, where resources and personnel are concentrated to assist as many injured individuals as possible in a short amount of time. Despite the best efforts, these large-scale events are often chaotic, making it difficult to detect critical conditions among the injured early, even though early detection would significantly increase their chances of survival. Therefore, emergency personnel must repeatedly check the vital signs of patients, which is especially challenging in stressful and understaffed situations.
The VitalKITE project builds on the findings of the FALKE and TeleSAN research projects, which demonstrated that it is possible to remotely capture vital parameters using various sensor technologies such as radar, IRT cameras, and RGB cameras, including drone-based methods. Additionally, advantages in overview and organization were identified through the 360° video transmission of a casualty collection point.
VitalKITE now integrates these prior insights into an advanced initiative aimed at providing a technical-scientific innovation to enable contactless monitoring of vital parameters in casualty collection points during large-scale disaster events. The goal is to develop a tethered "out-of-the-box" drone system that fully automates the real-time overview of patients' vital parameters within the treatment area, actively alerting personnel in case of critical conditions. This enhances patients' chances of survival and alleviates the workload of medical staff.
Cooperation partners
- Feuerwehr und Rettungsdienst Stadt Aachen
- Docs in Clouds TeleCare GmbH
Associated Partners
- Vectorbirds airbone systems GmbH & Co. KG
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Katastrophenmedizin e.V.
- Bundesamt für Bevölkerungsschutz und Katastrophenhilfe
- Malteser Hilfsdienst e.V.
- DRK-Rettungsdienst Städteregion Aachen gGmbH
Contact
Dr. med. Andreas Follmann (afollmannukaachende)
Tobias Martin, M.Sc (tmartinukaachende)
Lukas Ullmann (luullmannukaachende)
Funding
Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
Project duration: 05/2024 - 04/2026



KABINE- Mobile telemedizinische Untersuchungskabine zur Sicherstellung der ärztlichen Grundversorgung
Extremwetterereignisse wie zuletzt die Jahrhundertflut im Ahrtal 2021 verursachen großflächige Zerstörungen der gesamten Infrastruktur. Während und nach einer solchen Naturkatastrophe ist die medizinische Versorgung der Bevölkerung herausfordernd: da Krankenhäuser, Arztpraxen und Apotheken zerstört sind müssen andere Strukturen für die medizinische Versorgung aufgebaut werden. Der Bedarf an medizinischer Versorgung nach einem Katastrophenereignis ist sehr hoch und es mangelt im Katastrophengebiet an Ärzten, die vor Ort helfen können. Insbesondere die hausärztliche Versorgung können mobile Notpraxen nur bedingt abdecken. Neben Patienten mit akuten Verletzungen, wie Knochenbrüchen oder Verbrennungen, benötigen allerdings auch Patienten mit chronischen Erkrankungen wie Diabetes oder Bluthochdruck eine rasche und fachgerechte hausärztliche medizinische Betreuung.
Ziel von KABINE ist die Entwicklung eines Stufenplans zur möglichst raschen Wiederherstellung einer medizinischen Grundversorgung, d.h. einer hausärztlichen Versorgung, im Krisengebiet zu entwickeln. Kernelement ist hierbei die Entwicklung eines Demonstrators von telemedizinischen Untersuchungskabinen, die im Schadensgebiet aufgestellt werden können und dort in der Versorgung mit Strom und Kommunikationsmitteln autark funktionieren. In der Akutphase nach dem Katstrophenereignis soll die KABINE bei der Einteilung von Patienten in die verschiedenen Behandlungskategorien (Sichtung) unterstützen. In der Phase des Wiederaufbaus soll in den KABINE sehr frühzeitig eine normale hausärztliche und psychologische Versorgung der Patienten telemedizinisch angeboten werden.
Kooperationspartner
- Docs In Clouds TeleCare GmbH, Aachen
- Rudolf Riester GmbH, Jungingen
- Satellite Industries GmbH, Duisburg
- Björn Steiger Stiftung SBR, Winnenden
- DRK Kreisverband Ahrweiler e.V., Bad Neuenahr-Ahrweiler
- DRK Bundesverband e.V.
- Malteser Hilfsdient e.V. in NRW
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Katastrophenmedizin e.V. (DGKM), Kirchseon
Ansprechpartner
Dr. med. Andreas Follmann (afollmann@ukaachen.de)
Tobias Martin, M.Sc (tmartinukachende)
Anna Müller, M.Sc. (anna.mueller@ukaachen.de)
Förderung
Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, Rahmenprogramm Forschung für die zivile Sicherheit
Projektlaufzeit 04/2024 – 03/2026
Website
Polizeiärztliche Telekonsultation und Vernetzung mit dem Rettungsdienst zur Verbesserung der Handlungssicherheit in lebensbedrohlichen Einsatzlagen
Das Projekt PolARett zielt auf die Stärkung der Handlungssicherheit von polizeilichen Einsatzkräften in Bezug auf die medizinische Versorgung Verletzte bei „Lebensbedrohlichen Einsatzlagen“ (LebEl). Hierzu wird eine Software entwickelt, die die Anleitung der Einsatzkräfte entsprechend ihrer medizinischen Grundkenntnisse unterstützt. Auf unterschiedlicher Hardware, bspw. Smartphones, Datenbrillen und ähnliches kann diese Software zur telemedinischen Anleitung von Wechselschichtdienstlern und Spezialeinsatzkräften verwendet werden. Das übergeordnete Ziel ist die Verbesserung der Versorgungsqualität Verletzter durch eine frühzeitige Versorgung. Ergänzend wird die Schnittstelle zum Rettungsdienst und der Austausch von Informationen über diese Software betrachtet, um eine Übergabe der Auffindesituation und bisherigen Behandlung in kurzer Zeit aber ohne Informationsverlust durchführen zu können.
Kooperationspartner
- Polizei Rheinland-Pfalz
- Docs in Clouds Telecare GmbH
Assoziierte Partner
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Katastrophenmedizin e.V.
- Malteser Hilfsdienst e.V., Bildungszentrum Euregio
- Fachbereich Feuerwehr und Rettungsdienst Aachen, Stadt Aachen
- Deutsches Rotes Kreuz, Kreisverband Bitburg-Prüm e.V.
Ansprechpartner
Dr. Andreas Follmann
Förderung
Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung: https://www.bmbf.de/
Projektlaufzeit: 07/2024 – 06/2026


Das Projekt STREAM entwickelt einen digitalen, adaptiven und kontextsensitiven Anamnesebogen, der in telemedizinische Aufklärung integriert wird. Anhand eines Netzwerks von statistisch relevanten Fragen wird der Dialog individuell für jeden Patienten angepasst. STREAM verwendet KI und maschinelles Lernen, um eine vollständige, fehlerfreie Dokumentation sicherzustellen. Der Bogen ermöglicht die online Durchführung von Anamnesen und Aufklärungsgesprächen, reduziert Wartezeiten und unterstützt den Infektionsschutz. Durch Plausibilitätsprüfungen und die Nutzung hochgeladener Dokumente wird die Qualität der Patientenaufklärung verbessert.
Ziele
- Entwicklung eines adaptiven Anamnesebogens
- Integration in telemedizinische Aufklärung
- Nutzung von KI für personalisierte Fragenstruktur
- Verbesserung der Patientenaufklärung und Sicherheit
- Effiziente Planung medizinischer Ressourcen
- Nachhaltigkeit durch Verzicht auf Papier
Kooperationspartner
- Docs in Clouds TeleCare GmbH, Aachen
- RISK-CONSULTING Prof. Dr. Weyer GmbH, Köln
- FEHN Legal PartG mbB, Köln
Ansprechpartner
Benedikt Hürter
Förderung
Europäischer Fonds für regionale Entwicklung (EFRE) 2021-2027
Projektlaufzeit: 07/2024 – 06/2025

Interreg Meuse-Rhine Drone Emergency Network for Medical Logistics (EDEN-Medical)
Access to timely and reliable medical transport is critical, especially in emergencies where every second counts. In the border region, hospitals across national borders are often closer than domestic facilities, yet systemic differences hinder efficient transport of medical goods such as medicines, blood, and lab samples. Recent crises, including COVID-19, floods, and the Ukraine war, have highlighted these challenges, affecting stock management, deliveries, and lab capacity. Addressing these issues requires enhanced cooperation and innovative logistics solutions.
The EDEN-Medical project aims to establish a collaborative Urban Air Mobility (UAM) network for the swift and secure exchange of medical goods and information. By integrating drone-based logistics with an open, modular system, the project will improve medical transport and enable real-time data exchange between hospitals, drone operators, and medical teams. Additionally, the project will strengthen telemedical services, facilitating remote consultations and emergency coordination.
A key focus is identifying and addressing legal and regulatory barriers to cross-border medical transport. Concepts for hospital adaptation, automated drone integration, and necessary infrastructure will provide a roadmap for future implementation. Expected outcomes include faster, more efficient, and eco-friendly medical transport, enhanced crisis response, and expanded telemedicine access. Ultimately, the public will benefit from improved emergency healthcare services, increasing regional resilience.
Cooperation partners
The project is led by Uniklinik RWTH Aachen, in collaboration with RWTH Aachen University, Zuyderland Medical Center, Maastricht University, Ziekenhuis Oost-Limburg, Docs in Clouds TeleCare GmbH, flyXdrive GmbH, Aachen Fire Department, and DronePort Sint-Truiden.
Funding
Project EDEN-Medical is part of the Interreg Meuse-Rhine (NL-BE-DE) programme and co-financed with €1,703,544.55 ERDF, €592,761.54 by DE-Land NRW, and €27,978.62 by NL-Provincie Limburg.
Contact
Dr. med. Andreas Follmann (afollmannukaachende)
Dr. med. Sarah Veldeman (sveldemanukaachende)
Completed Research Projects (selection)

OR.NET – secure dynamic networking in operation room and hospital
Integration and networking in medical IT have been a great subject since years. Several projects deal with the networking of IT systems within a medical institution as well as overall facilities. An increasingly important aspect is the integration und networking of medical devices among each other and with adjoining IT systems. The project OR.NET addresses especially this core topic.
Goals:
- The development of certifiable, dynamic, non-proprietary networking possibilities in consisting and future devices
- Plug&Play Networking in consideration of aspects for approval capability and risk management
- Development of operator models
Further information can be found on: http://ornet.med-design.net
Cooperation partners
- Providers of integrated operation rooms
- Manufacturers of medical devices and medical technological components
- (IT-) service providers for software and IT solutions for networking
- Research Institutes, especially:
- Lehrstuhl für Medizintechnik (MediTec; Direktor: Univ.-Prof. Dr.-Ing. K. Radermacher)
- Lehrstuhl für Medizinische Informationstechnik (MedIT; Direktor: Univ.-Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dr. med. Steffen Leonhardt)
- Specialist clinic
- Klinik-IT-Abteilungen und Betreiber
Contact
Dr. Verena Voigt (vvoigtukaachende)
Funding
Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung
Project duration: 09/2012 – 08/2015


AUDIME – AUDIvisual medical information technology for complex emergency situations
Terrorist attacks, natural catastrophes and severe traffic accidents always bring serious challenges for rescue teams all over the world. Lack of information on number and severity of injured as well as information on available and necessary resources immensely impede the organisation of rescue operations and lead to relevant delays in patient transport and treatment.
The project AUDIME researches information technology-based decision and support systems including the relevant sighting algorithms for rescue procedures – from sighting up to the treatment at the treatment unit. Key requirements for the system are the usability in complex, supra-regional emergency situations, the integration capacity of existing and new support systems as well as a specific processing and provision of relevant information on the current situation. The technical project focus lies on the creation of an information-integration-system which, besides statistical data accumulation, enables the involvement and evaluation of continuous real-time data and telemedical aspects. In this way, relevant information is provided to the decision- and support system as well as all further networked users in real-time.
Cooperation partners
- Lehrstuhl für Informations-management im Maschinenbau (IMA) der RWTH Aachen
- Center for Security & Society, Institut für Soziologie Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg
- TECH2GO Mobile Systems GmbH
- GS Elektromedizinische Geräte G. Stemple GmbH
Contact
Dr. Andreas Follmann (afollmannukaachende)
Förderung
Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
Projektträger VDI Technologiezentrum GmbH
Project duration: 12/2014 – 12/2017

Postoperative pain does not only constitute a high acute burden on patients but also impedes the recovery and leads to chronicity. Therefore, an early detection and treatment of pain conditions especially in monitoring and intensive care units is significant. However, pain is a high-sensitive experience and therefore difficult to grasp despite different technical concepts (analysis of skin conductance, evaluation of heart rate variability and others).
The research project “Mimik” develops a system solution for long time monitoring of postoperative pain and stress in intensive care units. With the help of IR-thermography dynamic contours and thermal profiles of a patient’s face are measured in a passive and contactless way in order to detect reactions on pain stimulus (difference in facial expression, lacrimation, perspiration). Regardless of environmental conditions and networked with the hospital information system including secured data and long-term archiving this system will lead to an improved remote monitorability of intensive care patients.
The project’s goals:
- Detection of face shape and condition as well es changes in 3D with the help of IR-thermography
- Detection of pain reactions (changes in facial expression, lacrimation, perspiration)
- Medical evaluation of pain und stress reaction with derivation of therapy options
Cooperation partners
- RWTH Aachen Philips Lehrstuhl für Medizinische Informationstechnik (MedIT)
- RWTH Aachen Lehrstuhl für Bildbearbeitung
- Infra Tec GmbH
- Pneumatik Berlin GmbH Medical Systems
Contact
Henriette Dohmeier (hdohmeierukaachende)
Funding
Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Technologie
Projektträger ZIM- Netzwerkförderung
Project duration: 03/2014 – 01/2017


Leitwart – SmartCareUnit
Being part of the Smart Care Unit projects, this project is dedicated for the development of a system solution for a central control room with data fusion and interpretation across all devices in an intensive care unit. For this purpose, a fusion of medical devices and laboratory data across all manufacturers as well as data of the hospital IT should be enabled for the generation of smart alarm and decision support systems. At the same time, a software condition to master great, heterogeneous volume of data (video, audio, text, images, measurements) is developed (multidimensional databases, big data evaluations). A contactless, intuitive handling, highly complex data interpretation with recommendation for actions, stationary and mobile available and situation adapted visualization, trend based early alerting, secure documentation and long-term archiving characterize the new level of patient care. In this context, a special value is attached to usability, good medical design, data security and quality standards. The smart networked system solution for the intensive care unit offers more efficiency, value and life quality for patient and personnel.
Goals:
- Fusion of medical devices, laboratory data and hospital IT across all manufacturers
- Software development to master big, heterogenous volume of data
- Situation adapted visualization, trend based early alerting and data security in patient care
Cooperation partners
- Conworx Technology GmbH
- Yacoub Automation GmbH
- G.punkt medical services
- Dr. Hornecker Softwareentwicklung und IT-Dienstleistungen
- Fraunhofer Heinrich-Hertz-Institut
Contact
Dr. med. Verena Voigt (vvoigtukaachende)
Funding
Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Technologie
Projektträger ZIM- Netzwerkförderung
Project duration: 12/2014 – 05/2017


Wundscanner (Development of a mobile system for early detection and monitoring of wound infection)
Wound infections belong to the most frequent complications of medical interventions and cover around 24% of all nosocomial infections in Germany. First, they constitute a serious risk, not only for the concerned patients but also for fellow patients if not the whole hospital. In case of healthcare wound infections after interventions pose a substantial cost factor causing an additional cost of around 3 billion euros for over 220.000 infections per year. Second, the sooner the infection is detected the better and more effective treatment can be provided. Studies have shown that the thermal pattern of a wound in case of an infection exhibits special features. With the help of an infrared-thermography, these patterns can be assessed in a passive and burden-free way even before the inflammation gets visible for the human eye.
This project’s goal is the development of a scanner system that merges optical data of an infrared camera and a camera working within visible light and uses smart algorithms for image evaluation to create interpreted gradients over time and space.
Cooperation partners
- SANTOX Gehäuse-Systeme GmbH (https://www.santox.com/)
All cooperation partners are members of the ZIM-Network “AmbuCare”: https://www.smart-care-unit.de
Contact
Henriette Dohmeier (hdohmeierukaachende)
Franziska Schollemann, M.Sc. (mschollemannukaachende)
Funding
Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Technologie
Projektträger ZIM- Netzwerkförderung
Project duration: 10/2017 - 03/2020

The DFG research unit 2591 – a research consortium aims at defining a severity assessment framework for laboratory animals
Patients of the intensive care unit must be constantly monitored regarding their circulatory system and health status. For that, they are connected to necessary measuring instruments with the use of electrodes and derivations which takes time and severely narrows the patient’s ability to move. Even patient transport is thereby made more difficult. Through the development of reliable, contactless measurement methods the patients’ ability to move can in this regard stay unrestricted and clinical procedures can be optimized.
This study targets a contactless assessment of the health status of experimental animals. In a wireless way, vital data (respiration, pulse, temperature) can be measured, signs of inflammation can be checked and perfusion imaging can be performed with the help of video sequences, radar as well as infrared- and colour cameras.
Further information can be found on: https://severity-assessment.de
Cooperation partners
The DFG project is part of a DFG research group with the common title: “Severity Assessment in Animal-based Research” (FOR2591)
- P01 Prof. André Bleich, Phd, DipECLAM (Hannover Medical School, Institute for Laboratory Animal Science and Central Animal Facility, Hannover) und Dr. Christine Häger (Hannover Medical School, Institute for Laboratory Animal Science and Central Animal Facility, Hannover)
- P02 Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. René H. Tolba, MD, PhD (Institute for Laboratory Animal Science and Central Animal Facility RWTH Aachen University, Medical Faculty)
- P05 Prof. Peter Gass, MD (Central Institute of Mental Health, Mannheim, Mannheim Faculty / University of Heidelberg, Mannheim/Heidelberg)
- P08 Prof. Dr. Fabian Kiessling, M.D. (Chair of Experimental Molecular Imaging, RWTH Aachen University, Medical Faculty, Aachen)
- P10 Prof. Ute Lindauer, Dr. med. vet. (Translational Neurosurgery and Neurobiology, Department of Neurosurgery, RWTH Aachen University, Medical Faculty, Aachen)
- P11 Prof. Dr. Heidrun Potschka, DVM (Institute of Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Pharmacy, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Munich)
- P12 Prof. Kerstin Schwabe, Phd (Laboratories for Experimental Neurosurgery, Hannover Medical School, Department of Neurosurgery, Hannover)
- P14 Prof. Dr. Stefan Treue (German Primate Center, Head of the Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory, Göttingen) und Prof. Dr. Alexander Gail (Sensorimotor Group, German Primate Center, Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, Göttingen)
- P15 Dietmar Zechner, PhD (Rostock University Medical Center, Institute for Experimental Surgery, Rostock University Medical Center, Rostock) und Prof. Dr. med. Brigitte Vollmar (Institute for Experimental Surgery, Rostock University Medical Center, Rostock)
- nP17 Dorit Merhof, Prof. Dr. Ing. (Institute of Imaging & Computer Vision, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen)
- nP18 Marion Bankstahl, Prof. Dr. (Institute for Laboratory Animal Science, Hannover Medical School, Hannover)
- nP19 Nils Hoppe, Prof. Dr. (Centre for Ethics and Law in the Life Sciences, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität Hannover, Hannover) und Rebecca Knabb, PhD (Centre for Ethics and Law in the Life Sciences, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität Hannover, Hannover)
Contact
Dr.-Ing. Carina Barbosa Pereira (cbarbosapereukaachende)
Janosch Kunczik, M.Sc. (jkunczikukaachende)
Funding
Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Project duration: 03/2017 - 02/2020

MoVE – Modular Validation Environment for medical device networks
The integration and network of medical devices became an indispensable component of modern operating rooms during the last years. Especially big international manufacturers provide different monolithic solutions as overall systems. These systems though show a difficult to implement integrability with third party devices due to the necessity of conformity assessment of medical devices with the Medical Product Act as well as the risk management of networked medical products. Therefore, the market access for smaller and average manufacturers of medical devices is limited.
For the open networking of medical devices, adapted procedures and implements are absolutely required to support the approval process for manufacturers as well as the operation process for operators. The conception, implementing, validating and operation of such test areas for medical devices is complex and usually can’t be realised with reasonable costs by smaller and average manufacturers. These surroundings though prospectively are a significant component for a successful development of innovative products and their approval as well as their successful placement in the market.
Goals of this project:
- The development of a technical-strategical approach to support the approval and certification procedure and the risk management of networked medical devices in an integrated surgical surrounding
- The development of a test environment including appropriate protocols, scenarios and test areas as well as relevant approval strategies which are able to test the networking of medical devices and software components in different simulated scenarios and validate them regarding several parameters
- Further development of approval strategies for open networked medical products
Cooperation partners
- SurgiTAIX AG
- Localite GmbH
- Steute Schaltgeräte GmbH & Co. KG
- Fritz Stephan GmbH Medizintechnik
- Synagon GmbH
- Ilara GmbH
- Healthcare Consulting GmbH
- UTK Lübeck
- Lehrstuhl für Medizintechnik der RWTH Aachen (mediTEC Aachen)
- Institut für Angewandte Mikroelektronik und Datentechnik (IMD) der Universität Rostock
- Institut für Medizinische Informatik der Universität Lübeck
- Innovation Center Computer Assisted Surgery der Universität Leipzig (ICCAS)
Ansprechpartner
Dr. med. Verena Voigt (vvoigtukaachende)
Marian Ohligs, M.Sc. (mohligsukaachende)
Förderungen
Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
Project duration: 05/2018 – 09/2019
VirtualDisaster - Virtualized reality for tele-mission management in complex operational situations and major events


Large-scale disasters, such as terrorist attacks, major fire incidents or mass casualty incidents (MCI), always pose serious challenges to emergency personnel and incident commanders: Initially there is a lack of overview of the situation biasing the perception. It is often the overall perspective that incident commanders miss in order to determine lacking resources and available potentials.
In order to counter this problem, VirtualDisaster involves a tele-mission management, based on the model of the Aachen TeleMedic. Drones using 360° cameras and laser based distance meters (LiDAR) transmit three dimensional reconstructions of the scene. The use of virtual reality (VR) gives a quick overview of the scene even in difficult, inaccessible locations. The cooperation between the tele-mission management and the mission management (or the senior EMS physician) on site ensures a more efficient approach to the situation. This inevitably reduces delays in rescue and treatment of the injured, as well as in large-scale disasters.
Cooperation partners
- Berufsfeuerwehr Aachen
- TEMA Technologie Marketing AG
- RWTH Aachen, Institut für Flugsystemdynamik
- RWTH Aachen, Lehrstuhl für Informatik 8 (Computergrafik und Multimedia)
Contact:
Dr. med. Andreas Follmann (afollmannukaachende)
Marian Ohligs (mohligsukaachende)
Funding:
Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
Project duration: 07/2019 - 12/2021


FALKE (Aircraft assisted management of complex emergency operations)
In the case of an MCI (mass casualty incident), the emergency personnel’s main task contains the division of all injured into different sighting categories. Though many of the emergency personnel know the applicable sighting categories, it is often misapplied in an emergency operation. Reasons are among other things distraction and a psychological pressure in an acute situation.
To improve the sighting quality, this procedure is semi-automated within project FALKE. For that, different sensor systems (radar, IRT-camera, RGB-camera) are installed on an unmanned flying object to collect vital data and movement profiles as quickly as possible. Existent sighting algorithms are then adapted to the given data situation and corrected or confirmed by a telemedical attached senior emergency physician (Tele-LNA). Through a quickly developed situation image, the difficult sighting task gets semi-automated and further leads to early, focused and lifesaving immediate measures.
Further information can be found on: https://www.projekt-falke.org
Cooperation partners
- Docs in Clouds GmbH
- Lehrstuhl und Institut für Flugsystemdynamik, RWTH Aachen
- flyXdrive GmbH
- Lehrstuhl Integrierte Systeme, Ruhr-Universität Bochum
- IMST GmbH
Contact
Dr. med. Andreas Follmann (afollmannukaachende)
Lucas Mösch (lmoeschukaachende)
Funding
Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
Project duration: 08/2018 – 02/2022

hOspItal – Location-based information services in hospitals
Modern medicine is characterized by numerous diagnostic and therapy processes that interlock and require complex planning. In order to optimally take into account the socio-economic aspects of medical action, these processes should at the same time be organized and carried out as smoothly as possible. To achieve this goal, communication is required not only among medical personnel, but also between the personnel and the medical devices and objects in the hospital.
The hoSpItal research project wants to address this situation and improve the treatment processes in clinics with location-based information. In the project, an acoustic localization platform is to be researched, developed and used in a test environment, which solves the following tasks:
- Scheduling of the staff
- Localization of beds (for intra-hospital transports)
- Dynamic adaptability of the route graph
- Real-time calculation of arrival times
- Notify staff of arrival times
- Interactive treatment plan (e.g. replacement appointments in the event of non-appearance)
- Finding medical devices
- Positions of devices
- Number of free devices
- Predicting availability times
- Smart analysis
- Utilization of devices
- Capacity calculations (outlook)
Cooperation partner
- IT4process GmbH
- contagt GmbH
- Telocate GmbH
- Kinderklinik Universitätsklinikum Freiburg (associated partner)
Contact Person
dr.med. Milos Bogovac ()
Grant
federal Ministry of Education and Research
Funding period: 01/2020-04/2022
SteriRob - Sensor system for the identification and handling of sterile surgical instruments
In the course of the SteriRob project, the integration of service robots into the clinical sterile supply is to be pursued as a global goal. The primary goal of the project includes the development of a technical solution for the handling of the tray and various surgical instruments. The gripping process should be further supported by equipping the instruments with new types of RFID transponders, which allow exact identification and localization.
Both the increasing shortage of staff in the future and the time and cost pressure require the introduction of service robots into the supply of sterile goods. Due to the demographic change, the number of surgical interventions will continue to increase, which requires a time-critical provision of surgical instruments. In order to be able to deploy service robots in clinical use in the supply of sterile goods, however, different challenges have to be overcome, such as handling a wide variety of surgical instruments. In order to address this and other problems, an interdisciplinary consortium has been formed that comes up with coping strategies for the use of autonomous service robots in sterile goods supply.
Cooperation partners
- SurgiTAIX AG, Verbundkoordinator
- Aesculap AG
- Fraunhofer IMS
- ID4us GmbH
- IT4process GmbH
- Institut für Regelungstechnik, RWTH Aachen
- Lehrstuhl für Medizintechnik, RWTH Aachen
- Universitätsklinikum Essen
Contact
Dr. med. Nadine Hochhausen (nhochhausenukaachende)
Funding
Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
Project duration: 03/2019 – 02/2022
PriMed - Process optimization through integrated medical devices in operating theaters and clinics


As part of the PriMed project, there is a (further) development of concepts for the open networking of medical devices in the operating room and in the clinic with the aim of improving the perioperative processes. Based on the preliminary work of the OR.NET project, a flexible, context-adaptive process and treatment management system is to be created for the different anesthesiological workplaces.
Aims:
- Development of concepts for process optimization in the OR using integrated medical technology
- Expansion of an anesthesia workstation and application of the SDC open communication standard based on the results of the OR.NET project
- Contextual and situational presentation of information including the perioperative standard procedures, the different therapists and treatment centers
- Integration of decision support logic
Application of innovative human-machine interaction possibilities
Further information can be found at: http://primed.med-design.net
Cooperation partners
- SurgiTAIX AG
- Lehrstuhl für Medizintechnik der RWTH Aachen (mediTEC)
- Docs in Clouds GmbH
- IT4process GmbH
- Beger Design
- Localite GmbH
- Klinik für Neurochirurgie der Uniklinik RWTH Aachen
- OP-Management der Uniklinik RWTH Aachen
Contact
Dr. med. Verena Voigt (vvoigtukaachende)
Funding
EFRE NRW 2014-2020
Förderungszeitraum: 04/2019-04/2022



AIDA - Work development in elderly care through the introduction of a telemedical emergency service concept
Due to demographic change and the simultaneously prevailing shortage of skilled workers, across both nursing and medical professions, medical care in geriatric care facilities grows increasingly challenging. In case of a deterioration in condition, the attending general practitioner often is not instantly available for a home visit. Usually the following emergency call ends immediately in a hospital admission, even if the patients could often be treated further on an outpatient basis in their care facility.
In addition to the costs of hospitalization, this leads to far-reaching health-economic but also patient-related consequences, especially when demented patients are torn from their familiar surroundings.
In the AIDA project, a telemedical application (medical roll stand system TeleDoc) is used in the context of geriatric care in order to connect the general practitioners in charge of routine visits and emergency consultations via telemedicine, and to set up a 24/7 telemedical emergency service bridging the time the attending general practitioners is not available. The aim of AIDA is to make the medical and nursing staff capacities more effectively usable, to evaluate the changes in elderly care from an ergonomic point of view and to guarantee holistic patient care. The model project AIDA is intended to pioneer the broad practical introduction of teleconsultation in geriatric care facilities as basic and regular care.
Cooperation partners
- Uniklinik RWTH Aachen A.ö.R
- Docs in Clouds TeleCare GmbH, Aachen
- MA&T Sell & Partner GmbH, Würselen
- Stiftung Evangelisches Alten- und Pflegeheim Gemünd
- St. Gereon Seniorendienste GmbH, Hückelhoven
- Hausärztin Dr. Karidas-Moitzheim, Schleiden
- Hausärzte Dres. Schneider/Ferber/Kochs, Hückelhoven
- AOK Rheinland/Hamburg
Contact
Dr. med. Andreas Follmann (afollmannukaachende)
Dr. med. Sarah Veldeman (sveldemanukaachende)
Funding
Europäischer Fonds für regionale Entwicklung (EFRE) 2014-2020 „Investitionen in Wachstum und Beschäftigung“
Project duration: 11/2019 – 10/2022
TRAUM – Telemedical legal information and investigation methodology
An anesthetic briefing takes place prior to a planned surgical procedure with anesthesia. This discussion serves to educate the patient about the planned measures and the associated risks. In addition, a physical examination and the patient's individual medical history are recorded.
For the patient, this conversation is unfortunately often associated with long travel times and waiting times and, if the findings are missing, also with a new presentation in the clinic. In times of the COVID-19 pandemic, there is also a potential risk of infection with every hospital stay. The anesthesiologist has a high level of documentation effort, since documentation has to be documented several times, with increasing work density and an existing shortage of skilled workers.
In order to counteract this development, we have initiated a project: the telemedical legal information and examination method (TRAUM). The software specially developed for this enables the patient to conduct the anesthetic briefing from home and to fill out all related documents. For the anesthetist, the documentation effort is reduced and further process optimization measures are implemented.
Cooperation partner
- Uniklinik RWTH Aachen, department for anesthesiology, premedication clinic
- Uniklinik RWTH Aachen, Legal division
- Docs in Clouds GmbH
- Bavarian Health GmbH
Contact
- Dr. Andreas Follmann (afollmannukaachende)
- Jan Wienhold, Doktorand (jwienholdukaachende)
Grant
START – Forschungsförderung an der Medizinischen Fakultät der RWTH Aachen
Project duration: 04/2020 bis 03/2022

DIH-HERO - Digital Innovation Hubs in Healthcare Robotics
The European health sector offers great potential for the development of robotic technologies because of the numerous industrial sites in Europe as well as the medical progress and the needs of an aging society.
The main obstacles to the faster development of robotic solutions are high development costs and diverging national regulations. However, the global market requires rapid innovation.
Digital Innovation Hubs in Healthcare Robotics (DIH-HERO) therefore has the mission to create a sustainable network that connects the players in the health sector and to support small and medium-sized companies in the robotic health sector. Our goal is to accelerate innovation and reduce the time to launch robotic solutions in the healthcare sector. Therefore, the DIH-HERO online portal offers for example a good overview of 'services' to facilitate international cooperation.
DIH-HERO is an independent and sustainable platform for everyone who works in the healthcare sector. As the only hospital among the core partners of the project, the Uniklinik Aachen plays a vital role. The project started in January 2019 and is financially supported by the European Commission for 4 years with 16 million €. 8 million € of the funding will be invested in DIH-HERO's own tenders (https://dih-hero.eu/calls/) for SMEs. From January 2023, DIH-HERO will then continue to exist as an independent health network.
By connecting companies and players in the healthcare sector, DIH-HERO enables the development of innovative products and services for the healthcare market.
You can find more information on: www.dih-hero.eu
Cooperation partners
- University of Twente
- German Aerospace Center (DLR)
- Fraunhofer IPA
- CEA
- Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna
- Politecnico Milano
- Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia
- Tecnalia
- EURECAT
- Imperial College London
- Danish Technological Institute
- IMEC
- ETF Robotics
- Fundacja Rozwoju Kardiochirurgii
- ETH Zurich
Contact
Dr. med. Mare Mechelinck (mmechelinckukaachende)
Funding
Europäische Kommission (Horizont 2020; DT-ICT-02-2018)
Project duration: 01/2019 – 12/2022
TeleSAN - Telemedical Humanitarian Assistance to Ukraine
As part of the TeleSAN research project, telemedical humanitarian aid is to be provided in the current Ukraine war. Existing resources of the TeleSAN project were used and adapted for this purpose. The project is intended to review and evaluate the feasibility and use of telemedicine in civil defense and humanitarian aid. With the help of a cross-platform app, emergency services and helpers on site can communicate easily with volunteer doctors and CBRN experts from Germany and receive precise video-supported help in real time in individual and disaster medicine as well as operational organization areas.
Cooperation partners
- DGKM - Deutsche Gesellschaft für Katastrophenmedizin e.V.
- Uniklinik RWTH Aachen
- Docs in Clouds TeleCare GmbH
Contact
Dr. med. Andreas Follmann (afollmannukaachende)
Funding
Bundesamt für Bevölkerungsschutz und Katastrophenhilfe
Project duration: 04/2022 – 03/2023
VisiTemi – Telerobotics against loneliness in inpatient care for the elderly: a contribution to the COVID pandemic
Already before the COVID pandemic, almost every fifth person in fully inpatient facilities over the age of 80 in NRW mostly or (almost) always felt lonely. This is compounded by the fact that loneliness and social isolation, which has been reinforced by the ban on visits to senior institutions since March 2020, are risk factors of premature mortality. To counteract this, it is recommended as a preventive measure to maintain the existing social network individually and to strengthen it, for example, with modern communication such as video telephony.
In this project, the "Temi" robot system (distributed in Germany by Medisana GmbH) is to implement this video telephony and enable contact between residents of fully stationary facilities and their relatives. Increased by the humanoid appearance of the partially autonomous robot and its regular “visit”, loneliness is to be tackled acutely during the COVID pandemic. The scientific focus of the VisiTemi project is the evaluation of scientifically established questionnaires on loneliness and social isolation.
Cooperation partner
- Uniklinik RWTH Aachen, department for geriatric medicine
- Stiftung Evangelisches Alten- und Pflegeheim Gemünd
- St. Gereon Seniorendienste GmbH, Hückelhoven
- Medisana GmbH
Contact
- Dr. med. Andreas Follmann (afollmann@ukaachende)
- Franziska Schollemann, M.Sc. (fschollemann@ukaachende)
Grant
VisiTemi is associated with the AIDA project, but is funded from purely internal clinic funds. The robot system will be provided by Medisana GmbH free of charge for the period of the evaluation.
Project duration: ab März 2020
Optimal@NRW – Optimized acute care for geriatric patients through an intersectoral telemedical cooperation network - around the clock
The Optimal @ NRW project stands for a new intersectoral approach to the acute care of geriatric people in need of care. This approach includes the implementation of early warning systems, the provision of teleconsultation systems and the cross-sectoral digital treatment documentation in the 25 nursing homes belonging to the consortium. The project takes up the currently planned changes in emergency care and adds a "virtual digital counter", which is operated around the clock by the Uniklinik RWTH Aachen and the North Rhine-Westphalia KV. Specifically, this means that if a medical question arises in one of the participating nursing homes, teleconsultation with the virtual counter can be carried out via the medical call center (116117) after an initial medical assessment, or other assistance can be organized. In particular, if the family doctor is not available at this point in time and it is not an acute situation, mobile relief assistants (EVA) can support the local staff and provide medically delegable services in the context of visits to nursing homes. Thus, one of the central project goals, the avoidance of inadequate hospital admissions for outpatient-sensitive hospital cases (ASK) and improved medical care, should be achieved.
Consortium partner
- Barmer GEK
- Universität Bielefeld – Lehrstuhl für Gesundheitsökonomie & -management
- IKK Classic
- Techniker Krankenkasse
- DAK Gesundheit
- Kassenärztliche Vereinigung NordOst (KVNO)
- Itertalklinik Seniorenheim GmbH & Co. KG
- Senioren- und Pflegezentrum St. Antonius gGmbH
- carpe diem Gesellschaft
- JH Consulting
- Betreuungszentrum Arche Noah KG
- Wohn- und Pflegeheim Maria Hilf Burg Setterich GmbH
- Wohnanlagen für Senioren und Behinderte der “An der Zitadelle Jülich GmbH”
Contact
Pauline Weismann (paweismannukaachende)
Franziska Schollemann, M.Sc. (fschollemannukaachende)
Grant
G-BA Innovation Fund (Gemeinsamer Bundesausschuss)
Project duration : 01.04.2020-31.03.2024


TeleSAN – The tele-senior EMS physician as a strategy for the future of disaster medicine – a study testing the feasibility of telemedicine in civil defense
Civil defense emergencies of national importance such as terror attacks, military conflicts, fires and natural disasters as well as local disaster situations are challenging for emergency personnel and executives. Initially, there is a lack of overview, resources for medical treatment are missing and new dangers for both the comrades’ and the own life are omnipresent. Available human and material resources are primarily used for basic life support. Depending on the severity resource balancing might take several days only then allowing individual medical treatment. Aside from the patient care CBRN incidents and terror attacks pose further challenges demanding the immediate support from special forces.
This feasibility study aims at assessing the employment of telemedicine in civil defense emergencies following the example of the telemedicine system established in Aachen. After an evaluation the emergency personnel will be equipped with technical devices allowing them to connect with the tele-senior EMS physician (TeleLNA) as well as other tele-EMS physicians by use of a Tele-SAN app. They are immediately available and able to consult the on-site emergency personnel from afar without losing time about triage, first-aid and individual medical treatment such as the analgesia in cases of thermal traumas. Further specialists like Chemists or Policemen are also able to log on to the system in order to give advice without needing to be on-site. Not least, the TeleSAN-App should be available for the own smartphone providing professionals as well as first responders with treatment guidelines and instructions allowing them to take action within their means and to the best of their knowledge.
Cooperation partners
- Docs in Clouds TeleCare GmbH, Aachen
- Malteser Bildungszentrum Euregio, Aachen
- Rechtsanwalt Prof. Dr. Dr. Karsten, Köln
- Berufsfeuerwehr Aachen
- Deutsches Rotes Kreuz gGmbH Städteregion Aachen
Contact
Dr. med. Andreas Follmann (afollmannukaachende)
Anna Müller, M.Sc. (anna.muellerukaachende)
Funding
Bundesamt für Bevölkerungsschutz und Katastrophenhilfe (BBK)
Project duration: 05/2020 - 04/2023
Website
VitaSecure
The cooperation project "VitaSecure" is funded by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi) as part of the "Central Innovation Program for SMEs" (ZIM) with the aim of developing a multi-sensor solution for contact-free vital parameter monitoring in nursing homes.
The early detection of a critical patient condition, as is a matter of routine in the clinical setting through close vital parameter monitoring, should be established in the area of outpatient care in old people's and nursing homes. For this purpose, a system for contactless vital parameter detection is to be developed, which is based on the use of IR thermography and radar-based measurement technology.
Cooperation partners
Docs in Clouds TeleCare GmbH
IRPD GmbH
C & S Computer und Software GmbH
Klinik für Anästhesiologie, Uniklinik RWTH Aachen
Lehrstuhl für Integrierte Systeme der Ruhr-Universität Bochum
Contact
Tobias Martin, Arzt (tmartinukaachende)
Funding
Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz (BMWi)
Zentrales Innovationsprogramm Mittelstand (ZIM) - Netzwerkförderung
Project duration: 11/2021 – 04/2024

ProVital – Sensorbasierte Systemlösung für die Objektive Bewertung von Tierwohl und Stress in zoologischen Einrichtungen und privaten Haltungsformen
Die tierwohlgerechte Haltung von Zoo- und Wildtieren nimmt gegenwärtig einen zentralen Stellenwert im öffentlichen Diskurs ein. Die Bewertung von Stress und von Verhaltensmustern auf der Basis objektive erhobener Messwerte sind hier unverzichtbar. Gegenstand des Forschungsprojektes im Allgemeinen ist die Entwicklung eines automatisiert arbeitenden Monitoringsystems, welches ein kamerabasiertes Monitoring von Verhaltens-/Bewegungsmustern mit der berührungslosen Detektion von Vitalparametern und der Analyse von Akustikdaten kombiniert. Auf diese Weise soll die Bewertung des Verhaltens auf Basis eines spezifisch zu entwickelnden Tierwohl-Scores möglich werden. Über die Datenfusionierung im zeitlichen Verlauf werden softwarebasiert artgerechte Strategien generiert, um durch den gezielten, zeitlich definierten Einsatz von Elementen des Behavioural Enrichment Stress auszugleichen und ein Höchstmaß an Tierwohl zu bewirken.
Kooperationspartner
- Assion Elektronik GmbH
- Plecotus Solutions GmbH
- Docs in Clouds TeleCare GmbH
- Universitätsklinik Aachen AöR
- Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
- Fzmb GmbH
Ansprechpartner
- Lukas Breuer, M.Sc. (lubreuer@ukaachen.de)
Förderung
Zentrales Innovationsprogramm Mittelstand (ZIM) – Netzwerkförderung
Projektlaufzeit: 10/2021 – 05/2024